Galileo data reveal ammonia-bearing compounds on Europa
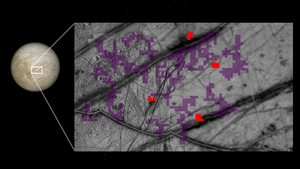
A recent reanalysis of data from NASA’s Galileo mission has identified ammonia-bearing compounds on the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa, a new paper reports. The results come from Galileo’s Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer observations made between 1995 and 2003 and were reported by researcher Al Emran of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Ammonia is a nitrogen-bearing molecule, and nitrogen is one of the elements important to life as we know it. The paper says this is the first detection of ammonia-bearing compounds at Europa and that the finding has important implications for the moon’s geology and its potential habitability, including its vast subsurface ocean.
The reanalysis turned up faint spectral signals of ammonia concentrated near fractures on Europa’s frozen surface, locations through which liquid water containing dissolved ammonia compounds would be expected to rise, the study finds. The paper notes ammonia lowers the freezing point of water—acting like an antifreeze—and that ammonia also has a short lifespan in the space environment.
Those qualities, together with the detection near large fractures and pits, suggest active placement of ammonia-bearing material from either Europa’s subsurface ocean or its shallow subsurface, the authors say. The study underscores the value of legacy datasets and modern analysis techniques, and it identifies a target for follow-up by the Europa Clipper mission, which is scheduled to arrive at the Jupiter system in April 2030.
ammonia-bearing compounds, europa, galileo mission, near-infrared mapping spectrometer, al emran, jet propulsion laboratory, europa ammonia detection, faint spectral signals, fractures on europa, europa frozen surface, subsurface ocean, shallow subsurface, cryo-volcanism, nitrogen-bearing molecule, active placement of ammonia, europa clipper follow-up, 1995–2003 galileo observations, legacy dataset reanalysis, modern analysis techniques, ammonia short lifespan, liquid water with ammonia, jupiter system arrival 2030
